5 Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance
Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria evolve to evade the effect of antibiotics through multiple different mechanisms. Resistance Mechanisms Defense Strategies Resistance Mechanisms Defense Strategies Description.

Emergence And Spread Of Antibiotic Resistance Part 2 React
Phenotypes Genotypes and Mechanisms if Glycopeptide Resistance in Enterococci The first report of enterococci resistant to high concentrations of glycopeptide antibiotics vancomycin and teicoplanin was published in 1988 when Uttley et al.
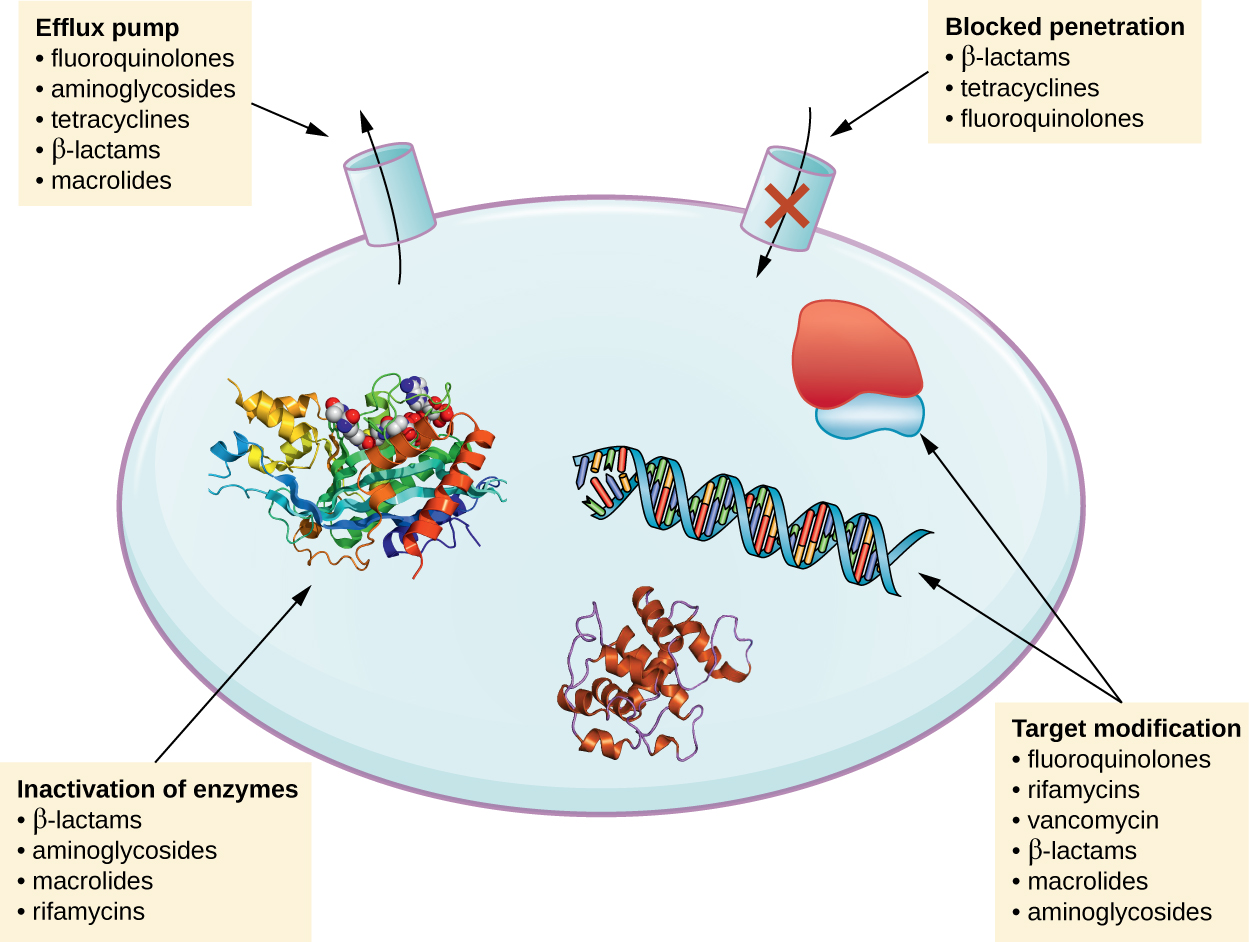
. New resistance mechanisms are emerging and spreading globally threatening our ability to treat common infectious diseases. These bacteria can. Certain bacteria are able to neutralize an antibiotic by altering its component to render it ineffective.
Antimicrobial-resistant infections that require the use of second- and third-line treatments can harm patients by causing serious side effects such as organ failure and prolong care and recovery sometimes for months. As previously noted enterococci exhibit significant resistance to a wide variety of antimicrobial agents. Antibiotic use in livestock is the use of antibiotics for any purpose in the husbandry of livestock which includes treatment when ill therapeutic treatment of a group of animals when at least one is diagnosed with clinical infection metaphylaxis and preventative treatment prophylaxisAntibiotics are an important tool to treat animal as well as human disease.
Resistance to even one antibiotic can mean serious problems. Antimicrobial categories are classifications of antimicrobial agents based on their mode of action and specific to target organisms. In addition adaptive antibiotic resistance of P.
Antibiotic resistance can be either plasmid mediated or mai. Antibiotic resistance genes ARGs are now regarded as emerging environmental contaminants Pruden et al 2006. This resistance is almost certainly relevant in most natural ecological settings in which enterococci dwell.
The MDR types most. Aeruginosa is a recently characterized mechanism which includes biofilm-mediated resistance and formation of multidrug-tolerant persister cells and is responsible for recalcitrance and. In this paper the authors discuss some mechanisms of antibiotic resistance such as changing the antibacterial agents uptake and biofilm formation as well as a wide range of approaches such as developing new generations of antibiotics combination therapy natural antibacterial substances and applying nanoparticulate systems.
This study aims to quantitatively elucidate the ARG enrichment on microplastics in aquatic environments with the comparison with other. Genome-wide association studies of global Mycobacterium tuberculosis resistance to 13 antimicrobials in 10228 genomes identify new resistance mechanisms. How the plastisphere affects microbial communities and antibiotic resistance genes ARGs is an issue of global concern.
Molecular Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance in Enterococci. PLOS Biology 2022. But the interaction mechanisms between ARG enrichment on microplastics and biofilm colonization stages have been not clarified.
The three fundamental mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance are 1 enzymatic degradation of antibacterial drugs 2 alteration of bacterial proteins that are antimicrobial targets and 3 changes in membrane permeability to antibiotics. The acquisition of drug resistance by P. Many medical advances are dependent on the ability to fight infections using.
Antibiotic resistance is rising to dangerously high levels in all parts of the world. Aeruginosa depends primarily on multiple intrinsic and acquired antibiotic resistance mechanisms including the biofilm-mediated formation of resistant and. Mechanisms of bacterial resistance to antibiotics Arch Intern Med.
Germs restrict access by changing the entryways or limiting the number of entryways. Dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes is an ecological and public health concern. Strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa are known to utilize their high levels of intrinsic and acquired resistance mechanisms to counter most antibiotics.
Faecium infecting patients in a hospital. As normal commensals of the human gastrointestinal tract enterococci are routinely. Multiple drug resistance MDR multidrug resistance or multiresistance is antimicrobial resistance shown by a species of microorganism to at least one antimicrobial drug in three or more antimicrobial categories.
Gram-negative bacteria have an outer layer membrane that protects them from their environment. 1 reported the occurrence of an outbreak of vancomycin-resistant E. Others might be able to export the antibiotics out.
Although this has been studied in aquatic ecosystems our understanding of. Restrict access of the antibiotic. A growing list of infections such as pneumonia tuberculosis blood poisoning gonorrhoea and foodborne diseases are becoming.

Mechanisms Of Antibiotic Resistance There Are Three Main Ways By Which Download Scientific Diagram
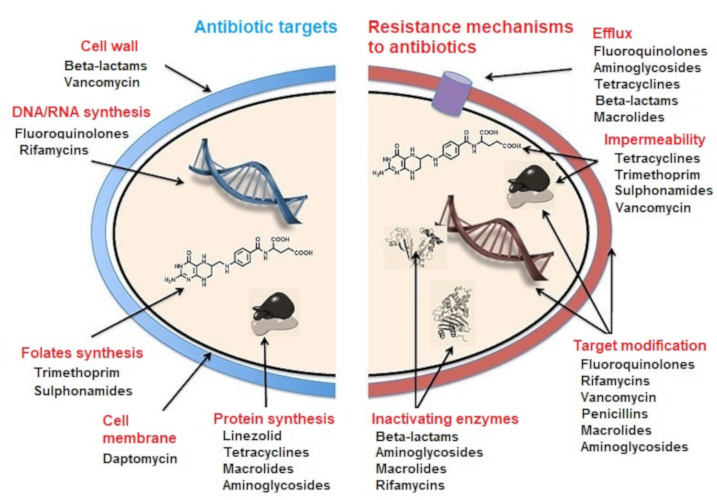
Antibiotics Antibiotic Resistance And Environment Encyclopedia Of The Environment

Microbiology Antimicrobial Resistance Learning Site

11 7 Mechanisms For Resistance Biology Libretexts
0 Response to "5 Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance"
Post a Comment